
Diagnostic Angiography in Thane- for Vascular Conditions of the Brain
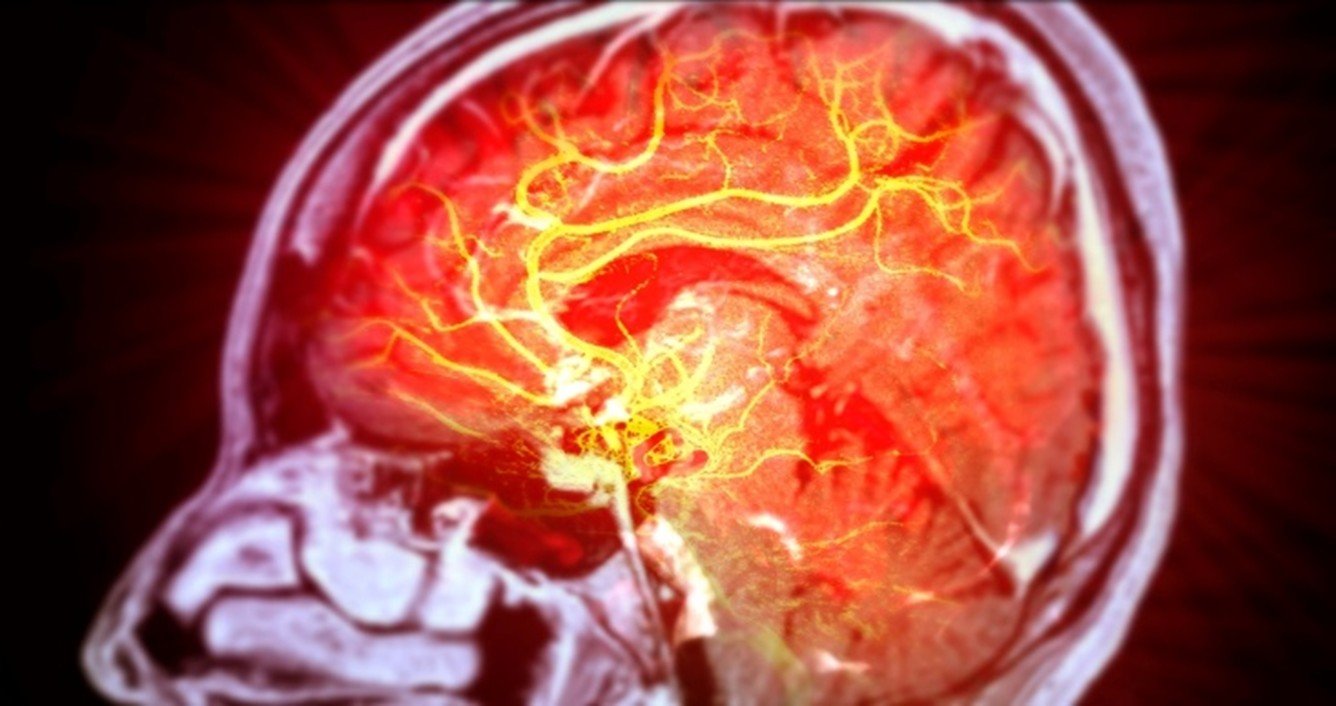
Diagnostic angiography in Thane is the most reliable test that doctors rely on when they need a clear look at the blood vessels in your brain. The advanced scan uses a special dye and X-ray imaging to show how blood flows through the brain in order to detect issues like aneurysms, AVMs, or blockages caused by strokes.
Diagnostic angiography is the most reliable test employed by doctors if they need to see a clear picture of blood vessels in the brain. This sophisticated scan depends on X-ray imaging and a special dye to outline the manner of blood circulation in the brain and help detect problems like aneurysms, AVMs, or strokes that lead to blockages.
Dr. Naren Nayak, a famous neurosurgeon in Thane, uses the latest imaging technology with a patient-first approach for diagnosing complex brain vascular cases and their treatment. Understanding how the test works will help you feel more confident and informed about your treatment options.
Get Clarity on Your Brain Health Today…
But how exactly does this treatment work, and why is it becoming a life-changing solution for many? Let’s explore further…
The Role of Diagnostic Angiography in Brain Vascular Conditions

Diagnostic cerebral angiography gives us a remarkably detailed look at blood vessels and is used for some pretty specific reasons when we’re trying to spot brain vascular issues. This is the gold-standard test for catching life-threatening conditions early and for planning out complex neurosurgical treatments.
Purpose and Indications of Cerebral Angiography
Diagnostic cerebral angiography provides an excellent and meticulous illustration of the blood vessels located in the head, neck, and brain. High-tech imaging enables the physicians to correctly identify the diseases impacting the circulation of blood, like the aneurysm, blockage, or other vessel troubles/vascular lesions.
This non-invasive method is regarded as the best way of diagnosing conditions that are related to brain cord vascularization and thus making it possible for doctors to make safe and effective treatment plans.
Some key reasons we do angiography:
Suspected cerebral aneurysms
Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs)
Checking for cerebral artery narrowing (stenosis)
Assessing vasospasm
Mapping vessels before neurosurgery
We rely on cerebral angiograms for both diagnosis and planning treatments. By combining what we see in the images with the patient’s clinical story, we can make smarter choices about what to do next.
Overview of Common Vascular Brain Conditions
Cerebral angiography is a procedure that enables the doctors to visualize the blood flow in the brain very well and detect conditions such as aneurysms, strokes, as well as the occurrence of blocked and tangled vessels. It is an important instrument that can be used for the purpose of treatment and surgery planning, thus ensuring patient safety.
Dr. Naren Nayak takes advantage of this intricate imaging to lead the way for accurate treatment, particularly in difficult situations where the tumor and the blood vessel are very close to each other.
Importance in Early Diagnosis and Treatment Planning
Diagnostic angiography in Thane is one of the most effective tools for detecting and managing brain vessel problems early — often making a lifesaving difference. Using Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA), doctor can clearly view blood flow in the brain, plan safer treatments, and even perform procedures like aneurysm coiling or stent placement during the same session.
Why it matters for treatment planning:
• Optimizes surgical approach – understanding vessel layout helps plan safer surgeries
• Identifies high-risk lesions – pinpoints areas that need urgent attention
• Guides procedural planning – helps select the best catheter routes and devices
• Predicts outcomes – shows if the brain has enough backup blood flow and how much tissue is at risk
Early detection through diagnostic angiography allows timely, targeted care and better recovery outcomes for patients.
Expert Brain Vascular Imaging by Dr. Naren Nayak…
Techniques and Procedures in Diagnostic Angiography

There are a few advanced techniques we use to get images of cerebral blood vessels. Each one has its own protocol for how we give contrast, prep the patient, and actually carry out the procedure. These days, we often combine classic catheter-based angiography with modern CT imaging for a more complete view.
Conventional Catheter Angiography Process
Catheter angiography is still the benchmark for seeing the brain’s blood vessels. We usually start by getting access through the femoral artery, using what’s called the Seldinger technique.
Steps before we get started:
Positioning the patient on the table
Injecting a local anesthetic where we’ll puncture
Setting up a sterile field and drapes
We thread a guidewire up through the arteries under fluoroscopy (that’s real-time X-ray). Then, we slide the catheter over the wire to the vessel we want to look at.
Doing selective angiography—where we pick out specific vessels—takes careful catheter placement. For smaller arteries, like the brachial, we’ll use a long, soft-tipped wire (usually about 300 cm).
The whole thing involves injecting contrast multiple times and capturing digital subtraction angiography (DSA) images. We take shots from different angles to get a full map of the vessels.
How we capture the images:
Anteroposterior and lateral views
Oblique shots if needed
High-res digital imaging
Fluoroscopy for real-time guidance
Contrast Material Use and Safety Considerations
Catheter angiography use iodinated contrast agents. These days, we go for iso-osmolar or low-osmolar agents to cut down on bad reactions.
Picking the right contrast:
Iodine concentration (usually 300-370mg/ml)
Osmolality
Viscosity
Any history of allergies
Before the procedure, we always check kidney function (serum creatinine) and figure out the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) to see if there’s a risk of contrast-induced nephropathy.
If a patient’s eGFR is below 30ml/min/1.73m², we’re extra careful—maybe using less contrast or switching to a different imaging method altogether.
Safety steps we always follow:
Document any allergies
Pre-medicate high-risk patients
Make sure patients are well-hydrated
Keep a close eye on them afterwards
We keep emergency medications on hand at all times—antihistamines, steroids, and resuscitation gear, just in case.
Preparation and Recovery for Patients
Getting ready for angiography starts with a full patient assessment and a thorough conversation about consent. We check medical history, current meds, and any past reactions to contrast.
Before the procedure, patients should:
Not eat or drink for 4-6 hours
Have baseline blood tests (FBC, U&Es, clotting)
Go over their medications—sometimes adjustments are needed
Have IV access placed
The whole angiography usually takes about 30-60 minutes, depending on how complex things are. We watch patients closely the entire time.
Afterwards, care is all about checking the puncture site and watching for any neurological changes. Patients usually need to lie flat for 4-6 hours after catheter angiography to prevent bleeding.
During recovery, we:
Check the puncture site every 15 minutes at first
Feel for pulses beyond the site
Monitor blood pressure and heart rate
Keep an eye on neurological status
We encourage patients to drink plenty of fluids to help flush out the contrast. Most patients are back to their normal routines within a day.
Before going home, patients get written instructions about caring for the puncture site and when to call us if something seems wrong. Follow-up depends on why we did the angiography and what we found.
Clinical Insights and Expertise: Dr. Naren Nayak's Approach

Dr. Naren Nayak invariably stays accurate, and well-planned, and treats in a very humane way when he is going to diagnose the complicated conditions of the brain vessels. He makes use of the advanced endovascular and microsurgical techniques and makes it sure the patient receives safe and personalized care—be it an aneurysm, a pituitary tumor, or a movement disorder associated with the vascular problem.
Specialised Care in Complex Brain Vascular Cases
Dr. Nayak’s technique is all about careful vessel mapping and then conducting safe surgical planning for the complex brain vascular cases. He looks into the blood flow patterns very thoroughly so that he could provide not only to the patients a good treatment but also a safe one while having the doctors a good diagnosis through his treatments.
The significant parameters involved in the diagnosis are:
Assessment of tortuosity of the vessel
Evaluation of flow dynamics
Identification of collateral pathways
Haemodynamic stress analysis
Dr. Nayak has been practicing for quite a long time in the neurosurgery field, and he can thus combine real-time angiography with the less invasive endovascular technique—cutting down the recovery time while precision and safety are still guaranteed.
Pituitary Adenomas and Aneurysms Management
Frequently, pituitary adenomas are positioned quite close to the major brain vessels, thus accurate angiographic planning is very important. Dr. Nayak utilizes sophisticated imaging techniques to analyze the locations of arteries and veins prior to the operation, which results in risk reduction and improved outcomes.
Angiographic examination primarily concerns:
Encasement of internal carotid artery
Participation of cavernous sinus
Patterns of venous drainage
Evaluation of collateral circulation
His comprehensive vascular mapping contributes to a safer endoscopic tumor removal — ensuring the preservation of essential neurovascular structures during the whole operation.
Progress and Results in Cerebral Vascular Imaging

Contemporary digital and AI-based imaging have completely transformed brain vessel diagnostics, thus making neurosurgeries more safe and accurate.
Latest Advancements in Imaging Modalities
The imaging tools available today such as 3D/4D Angiography, CTA, and MRA are capable of offering extremely detailed, real-time visuals of the blood flow in the brain — this helps in very early detection of problems and accurate planning of interventions.
Major technical advancements:
Image resolution much sharper
Significantly lower radiation exposure
Reduced scan times
Use of safer contrast agents
These developments in the field of imaging are also accompanied by an improvement in the planning of neurosurgery and outcomes.
These advancements are making it easier for neurosurgeons like Dr. Nayak to plan more intelligently, perform surgery under even safer conditions, and provide better results for patients.
Benefits to pre-operative planning include:
Determining the size and location of the aneurysm with great accuracy
Mapping the AVM accurately
Assessing the collateral circulation
Better prediction of surgical risk
Improvements in clinical outcomes:
Reduced surgery time and quicker recovery
Reduction of complications in aneurysm cases
Increasing stroke treatment success rates
Planning for endovascular procedures becoming more accurate
By combining different imaging methods, we get a full picture of the brain’s blood supply. These days, it’s possible to match up detailed angiograms with functional imaging, so treatment can be tailored without sacrificing neurological function.
Wondering If You Need a Brain Angiography? …
Frequently Asked Questions
What are indications for performing a diagnostic angiography in the case of vascular conditions of the brain?
Diagnostic angiography provides a detailed view of brain blood vessels, helping detect conditions like aneurysms, AV malformations, and strokes, and guiding surgery planning when regular scans aren’t enough.
How does diagnostic angiography help in the management of cerebral vascular disorders?
Catheter angiography is the gold standard for assessing brain, head, and neck vessels, offering precise mapping and real-time blood flow insights to guide effective treatment.
What are the possible risks or complications of cerebral diagnostic angiography?
Diagnostic angiography is generally safe, with rare risks like bleeding, infection, or stroke (less than 1%). Strict safety measures are always followed to protect patients during the procedure.
Can you walk me through the steps concerning diagnostic angiography with regards to cerebral vascular conditions?
A cerebral angiogram takes about 1–3 hours, using a catheter and contrast dye to capture X-ray images of brain blood vessels. The insertion site is then carefully sealed to prevent bleeding.
What are the considerations for aftercare following the angiographic procedure?
After a cerebral angiogram, patients are monitored for a few hours, advised to rest, avoid heavy activity for 24–48 hours, and report any unusual symptoms immediately.
Disclaimer: The information shared in this content is for educational purposes only and not for promotional use.
